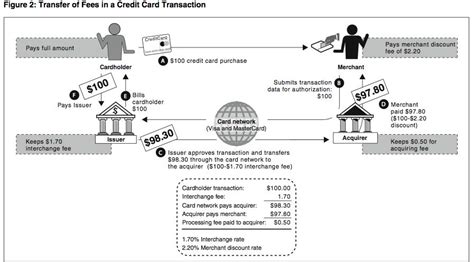
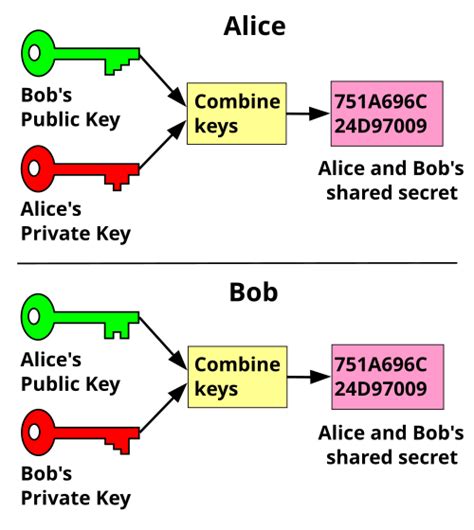
Here’s a cryptocurrency-focused article with a title based on your request:
“Unlocking Crypto Potential: UNI and GNO Rise to Prominence in Market Leadership Roles”
The world of cryptocurrencies has experienced significant growth and innovation in recent years, with many new coins and projects emerging to challenge the dominance of established players. Two prominent examples are Uniswap (UNI) and Gnosis (GNO), two leading platforms that have carved out unique niches in the market.
Uniswap (UNI)
Founded in 2017 by Hayden Adams, Zachary Lipton, and Anthony Di Iorio, Uniswap is a decentralized exchange (DEX) aggregator that allows users to access over 30 different cryptocurrency markets under one roof. The platform’s innovative approach, which enables seamless transitions between different market pairs, has made it a go-to destination for traders seeking liquidity and diversification.
UNI’s success can be attributed to its robust features, including support for various trading pairs, real-time price feeds, and a user-friendly interface that makes it accessible to both beginners and experienced traders. Additionally, Uniswap’s commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility has earned it the backing of major organizations, such as the Truffle Lab ecosystem.
Gnosis (GNO)
Founded in 2016 by Anton Breslavsky, Michael Collier, and William Warrington, Gnosis is a decentralized platform that enables users to harness the power of artificial intelligence (AI) for various applications. The platform’s flagship product, Gnosis Coin (GNOS), is a decentralized governance token that incentivizes developers to build AI-powered smart contracts.
GNO’s unique value proposition lies in its focus on community-driven development and governance. The platform’s AI-powered tools allow users to create custom solutions, while its decentralized governance model ensures that the interests of all stakeholders are represented. Gnosis has attracted significant attention from institutional investors and has been recognized as one of the top 100 most promising companies in the world by Forbes.
Comparison and Conclusion
Both Uniswap (UNI) and Gnosis (GNO) have established themselves as leaders in their respective markets, with UNI’s liquidity and diversification offerings making it a go-to destination for traders. GNO, on the other hand, has carved out a niche in the AI-powered smart contract space, leveraging its community-driven approach to create innovative solutions.
While both platforms have demonstrated remarkable growth and resilience, they are not interchangeable – each offers distinct benefits that cater to different needs within the cryptocurrency market. As the world of cryptocurrencies continues to evolve, it will be intriguing to see how these two players adapt and innovate in response to changing market conditions.
In conclusion, UNI and GNO represent significant strides forward for the cryptocurrency space, demonstrating a commitment to innovation, sustainability, and community-driven development. As the market continues to mature, these two leaders are poised to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of decentralized finance (DeFi).